Insurance Policy Definition Economics
This breaks the usual pattern of commercial policies being tied to specific vehicles and of personal policies alone being tied to individuals. The insured by paying a definite amount in exchange for an adequate consideration called as premium.
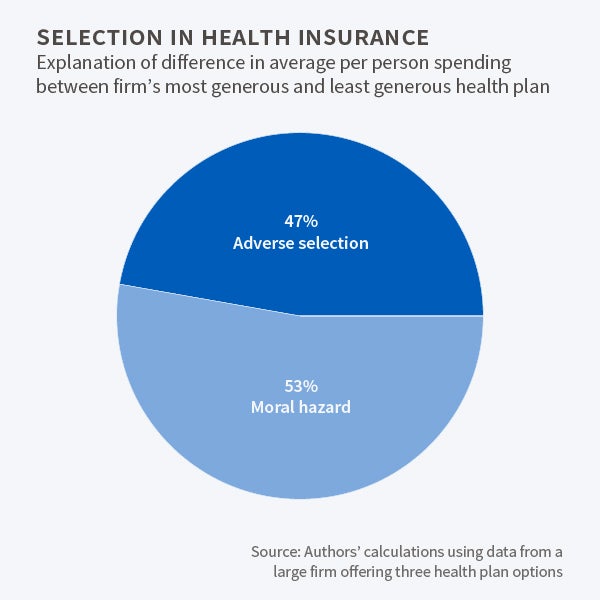
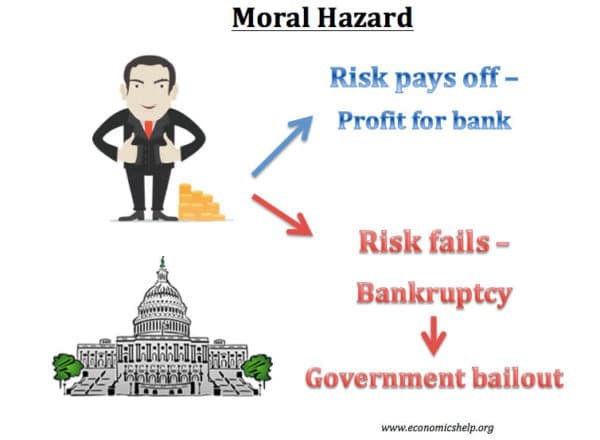
Moral Hazard And Adverse Selection In Health Insurance Nber
There many types of.

Insurance policy definition economics. Part One of the policy covers the employers statutory liabilities under workers compensation laws and Part Two of the policy covers liability arising out of employees work-related injuries that do not fall under the workers compensation statute. Insurance Annualized Premium Return Beneficiary Annuity Insurable Interest Insurability Claim Amount. Life insurance offers protection against the economic impact of an untimely death.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Moreover commercial insurances do not have for its object the maintenance of a minimum standard of living which is the only inspiring motive of social insurance. The risks covered and amount of money paid for losses under an insurance policy.
Insurance refers to a contractual arrangement in which one party ie. Life insurance is a contract between an insurer and a policyholder. Waiting period in which the insurance benefits do not apply is also a type of exclusion.
The owner of an insurance policy. A basic economic tenet of insurance including health insurance is the relationship of the price of the insurance to the individual usually in the form of a regular insurance payment called a premium to the likelihood of the individual filing a claim. Insurance company or the insurer agrees to compensate the loss or damage sustained to another party ie.
Health insurance covers the sometimes extraordinary costs of medical care. A life insurance policy guarantees the insurer pays a sum of money to named beneficiaries when the insured policyholder dies in. The person or organization seeking to transfer risk the insured policyholder pays a relatively small amount the premium to an insurance company the insurer which issues an insurance policy in which the insurer agrees to reimburse the insured for any losses covered by the policy.
Method of protecting a person from financial loss whereby policy holders make regular payments to an insurance entity. And bank deposits are insured by the federal government see financial regulation. The company or agency that writes an insurance policy.
In commercial insurance the policy benefits are according to the premiums paid while in social insurance the benefits received by the workers are much larger than their contributions. Generally there are two types of such agents who reach the prospective parties that may be interested in buying insurance. The insurance firm then remunerates a group member who suffers significant financial damage from an event covered by the policy.
The out-of-pocket money paid by the policyholder before an insurance company will cover the remaining costs. An agent is a person who represents an insurance firm and sells insurance policies on its behalf. An insurance policy that provides coverage for an employers two key exposures arising out of injuries sustained by employees.
In general terms governments are concerned with at the macro-level securing full employment see UNEMPLOYMENT price stability see INFLATION ECONOMIC GROWTH and BALANCE OF PAYMENTS equilibrium and at the micro-level an. Economic Loss Doctrine a legal principle that precludes recovery by an injured party for purely economic damages if there is no privity of contract with the tortfeasor. Insurers are able to provide coverage for virtually any predictable loss.
The one who pays the premiums. What is would cost to replace a piece of property or rebuild a structure. Insurance plays a central role in the functioning of modern economies.
Economic policy The strategies and measures adopted by the government to manage the economy as a means of achieving its economic objectives. Social insurance definition is - protection of the individual against economic hazards such as unemployment old age or disability in which the government participates or enforces the participation of employers and affected individuals. Insurance is a contract policy in which an insurer indemnifies another against losses from specific contingencies or perils.
This argument has been used by design professionals to avoid liability for claims by contractors tenants and others who suffered economic loss as a result of design errors or omissions. Start studying Economics Insurance Terms.
/GettyImages-1053743626-3b1327252ce94a998c9508c06fed8eea.jpg)
How To Easily Understand Your Insurance Contract

Choices Involving Risk Ppt Download

Whole Life Insurance Definition

Is There A Link Between Economic Growth And Insurance And Banking Sector Activities In The G 20 Countries Sciencedirect
/life_insurance_151909996-5bfc371046e0fb005147a943.jpg)
How Cash Value Builds In A Life Insurance Policy

Insurance Definitions Features
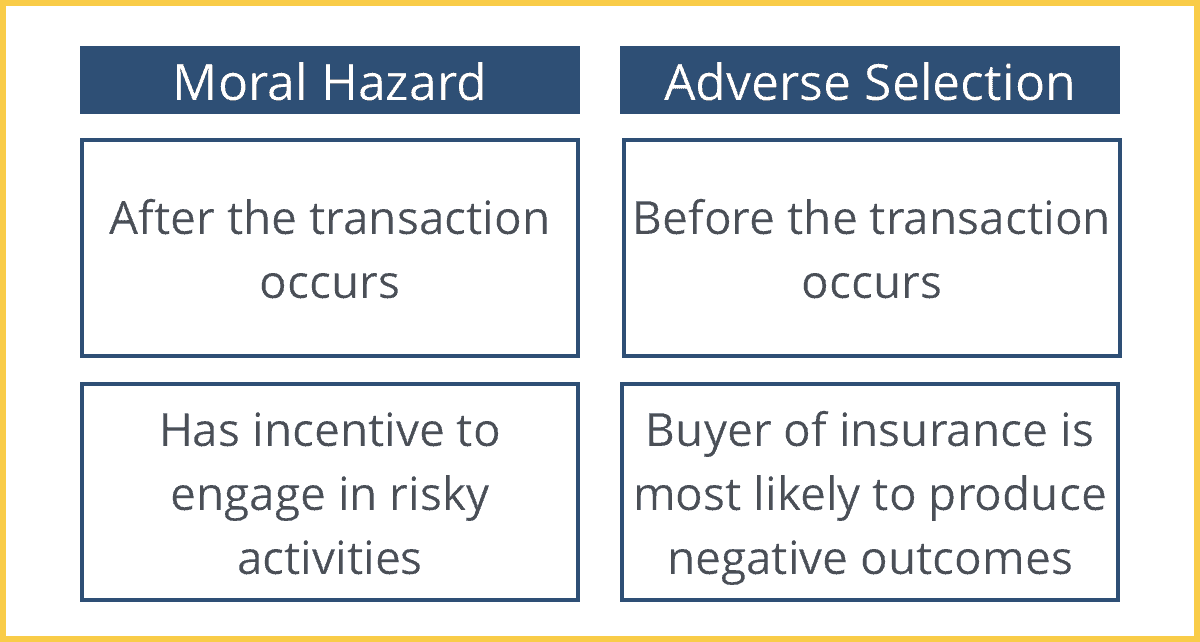
Adverse Selection Intelligent Economist

What Is Life Insurance Exact Definition Meaning Of Life Insurance

What Is Insurance Definition Types And Principles Business Jargons
/laissez-faire-definition-4159781-V2-828107953ee443f1bdeaaaba9b35759b.jpg)
What Is Laissez Faire Economic Theory
Life Insurance Guide To Policies Companies
Https Www Jstor Org Stable 24563243

Pin By Investopedia Blog On Finance Terms Negotiable Instruments Life Insurance Policy Business Law
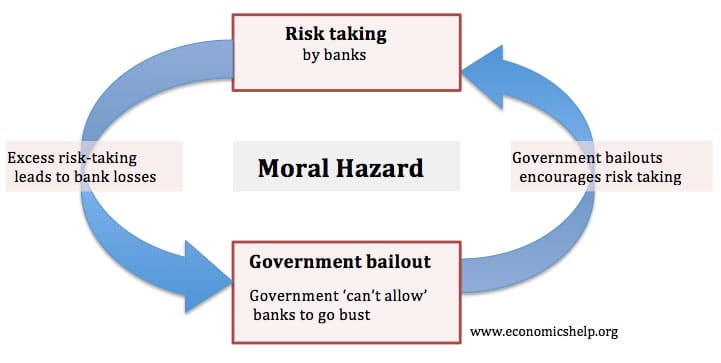
/types-of-insurance-policies-you-need-1289675-Final-6f1548b2756741f6944757e8990c7258.png)
/GettyImages-1036290704_2400-a0add133324a4892b365358ab661634e.jpg)
/GettyImages-1141164585-5486d44770c94a2784185a75be37a6fa.jpg)
/GettyImages-1134608493-a72c93c4adc34ee3b5a1c6e54dffa379.jpg)
Post a Comment for "Insurance Policy Definition Economics"